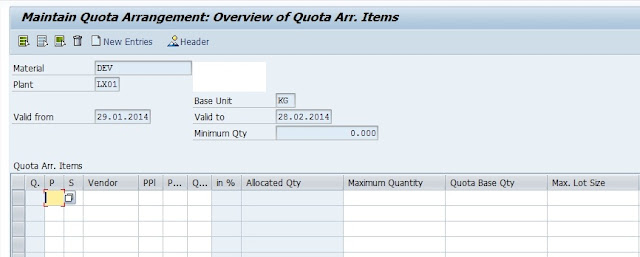
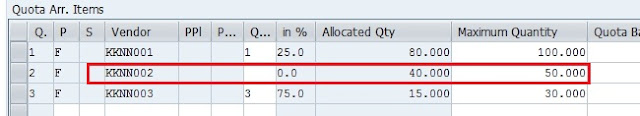
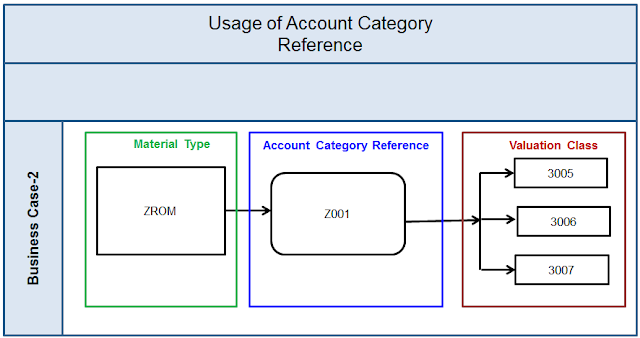
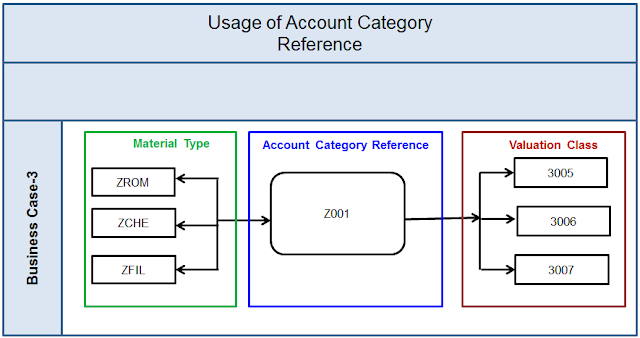
There are many business cases for S/4HANA Adoption for existing SAP Customers. However, the journey to S/4HANA Business Suite is fraught with its own challenges which are inevitable – the costs and risks of migrating and upgrading to a new system, especially for those customers, who have built very complex and distributed landscapes spanning across geographies and businesses.
One element of S/4HANA, which has caught the imagination of many of the Global Customers is Central Finance, which has been projected as the “Smartest”, “Fastest”, “Simplest” way to latch on to S/4HANA bandwagon with a quick win of simplified and unified financial reporting structure. The approach of Central Finance, instead of forcing customers to migrate their SAP instances to S/4HANA Application, allows financial documents to be replicated into a new Central Finance instance running on S/4HANA Business Suite. This is particularly true for Customers who have multiple old SAP ERP Instances and non SAP Systems as well. This gives an organization wide financial reporting view, with minimal intervention to the Transaction Processing Source SAP and non SAP Systems. It has been claimed to be a quick win solution for all the Enterprise Customers of SAP, with extremely short turnaround time for adaption.
However, there are series of multiple challenges, which need to be considered in implementation of Central Finance. Some of them can dearly cost the S/4HANA Journey and cost thousands of dollars in terms of effort and missed objectives. Some of the business related challenges and technical product related challenges that I have encountered in my journey on Central Finance Project are below:
1. Organizational Structure: One of the biggest use cases for central finance is to look at harmonized reporting for multiple markets. A logical extension of central finance on S/4HANA is to use the same CFIN System as a future Business System with integrated Finance and logistics transaction system. Therefore, it makes the organizational structure design extremely critical. In one of my projects, the customer in the legacy ERP (Source SAP ERP Systems) was using Business Area, Segment, Profit center etc as key considerations for reporting. Additionally, the Logistics Org Structures like Sales Org were not having in synch in various Source ERP System, as well as non SAP Source system did not have the org object which were relevant from SAP standpoint. As an IT Strategy roadmap, the customer wanted all the markets, where it operated to be on S/4HANA Business Suite and CFIN was the starting point. Additionally, many of the org structures were used in Account Based COPA in CFIN. So the Organizational structure design is a very crucial factor for long term journey and it is critical that design of org structure is thought through in CFIN. This should take into consideration the future logistics org structure as well
2. New GL and Document Splitting in S/4HANA Central Finance: Document splitting and parallel ledgers functionality is one of the key asks from Finance Transformation for a large scale Enterprise level customer. Many of the customers might be using a source system without functionalities like new GL or Document splitting, but would want to use the S/4HANA CFIN with these functionalities. However a source system without Document splitting for eg and a target CFIN System with Document splitting is NOT a functionality which is supported out of box. It takes a real challenge to make sure that all the documents replicated from the source SAP ERP and non SAP Systems have the right level of details to support Document splitting. There are options available like BADI_FINS_CFIN_AC_INTERFACE, which can be used to enable the right rules for populating the account assignments for Document splitting. Some of the examples for Document splitting and parallel ledger usage:
◈ The account assignments for Document splitting can be populated only in some of the line items and let standard Splitting set up take care of offsetting line item (eg, Profit Center and segment update in line items and let vendor line item derive the same from offsetting line item in case of Vendor Invoice Posting).
◈ Some of the FI Document line items can derive account assignment objects for document splitting from areas like material master, cost center etc. The customer specific changes, should not be triggered in case, where standard derivation logic can work
◈ Secondary CO Postings from Source systems, where the profit center is not available in one of the line items, the customer specification needs to be updated
◈ Data from Non SAP systems needs to be enriched with account assignment details for postings in the target central finance system
◈ There are transfer postings between subledgers which fail in the target system if it has document splitting active.
3. Master Data Harmonization: Master data replication of objects like Cost Center, Profit center, GL Accounts, customers, Vendors etc is a challenge. Data harmonization is a key challenge in Enterprise customers with multiple SAP Systems. Some of the challenges in master data set up in Central Finance encountered in my experience are:
◈ Customer Vendor Integration - The central finance function was used in S/4HANA 1610 EM instance, where the customers and vendors are created as Business Partners and the number ranges were overlapping in the source system for Customer and vendor account groups. To tide over the issue, the number ranges for Vendors were changed in the target CFIN System
◈ GL Master Data Replication - The SAP ERP System were substantially old systems, where transactional data existed for more than 15 years. As part of CFIN replication, only few years of historical data was being replicated into the target CFIN System. So the GL Master replication was designed based on the no of years in past where transactional data existed for a GL, that only was replicated into the target system
◈ Profit Center and Segments – One of the outcome of org structure redesign in CFIN was the whole profit center and segment usage in Central finance. The profit center in target CFIN system was tagged to Brand for reporting, while a segment was concentrated around line of business. However, the brands in the source system were limited to profit center with Business area being used for line of business reporting. The usage of different objects for reporting in source and target system entailed usage of complex mapping framework for replication of master data
◈ Material master – The material master usage was also a challenge due to disparate systems. A governance structure was required to be put in place to synch up the master data in the source systems and than have the same replicated in the target system.
◈ Data Services or SLT for Master Data – Harmonization and Business Objectives for Master data usage greatly determined the usage of the technology layer for replication between Source SAP and non SAP Systems to S/4HANA Central Finance Environment. Based on specific requirements like Data Filters for GL Account, Numbering changes etc, it was decided to introduce Data Services as a technology layer between Source and Target system for master data replication in S/4HANA Master Data replication.
1. MDG Layer and Value / Key Mappings: Central Finance offers an integrated MDG layer which can be used to recreate the accounting document in the target system, based on the data replication from the source. Some of the key learnings from my association with the central finance project were:
◈ Mapping Action - The mapping action determines if a transformation is required for any data element. In one of my project, business area was very widely used for financial reporting in the source SAP system. However, the complete reimagining of financial reporting meant that business area was not a key reporting factor in Central Finance. Hence a mapping action was set to clear the business area information from the source data. Essentially, the Mapping action should be designed taking into consideration of what are the key financial reporting parameters and if those parameters will hold true for the business even in case of a completely integrated system of records with finance and logistics transactions happening in the same system some time into future.
◈ Key Mapping - Typically the identifiers for a business object can be different in source and target system, given that Central Finance has the ability to connect to a heterogeneous set of SAP and non SAP systems. Eg, a customer 2212 in a source system may be customer (BP) 500000 in CFIN to harmonize master data. In one of the projectw, the key ask was to manage millions of customer master, vendor, gl etc to name and arrive at a common structure. The current design of central finance does not support automatic mapping of the source and target object number, though there is a standard upload tool to do an excel upload using the transaction code FINS_CFIN_MAP_MANAGE. However, to manage the real time replication of master data in the mapping layer, a custom program was created for each of the object to ensure, that there are no failures in transactions
◈ Value Mapping Structure - The value mapping is used in Central Finance to ensure if any transaction specific value has to be transformed. In some of the projects, the source systems had custom values for objects like Document types, Tax Codes etc. The whole objective of the transformation program was to ensure a standardized approach to finance structure across multiple markets. Eg, the markets used Document type R1 and RX for billing in two different geographies, but the intention in the target central finance system was to ensure that all the geographies, where the business operated should have the same document type for billing transactions. Hence the value mapping functionality was used to ensure that the new system has a standardized approach
2. COPA Transformation from Costing based COPA to Account based COPA: Most of the customers in SAP World use Costing based COPA. However, the preferred approach for reporting in S/4HANA Is Account based COPA. The data replication from the Costing based COPA to Account based COPA is not a standard and out of box functionality in S/4HANA. Some of the challenges encountered have been:
◈ There are scenarios in CB COPA where COPA data and GL postings happen at different time, whereas the expectation on AB COPA is to have the data based in COPA and GL at the same time. This presented it’s own challenges since AB COPA was supposed to be used for all kind of profitability analysis. Some of the design considerations for this transformation included moving key data like Sales Area data, material product hierarchy etc from material master, customer sales area data into central finance. These attributes were used in the derivation rule to ensure that the right attributes are populated. In some of the scenario like post goods issue, the data which is relevant for COPA was pulled through custom enhancements into Central finance.
◈ There are condition types on the billing cycle, which post data into COPA but not into GL. This functionality is not yet supported in AB COPA in S/4HANA. This means that the business had to look at the way, in which some of the discounts and pricing could be extended to Billing cycle
3. Transactional Data Posting: Central finance is supposed to reflect all of transactional financial data into a single place from multiple systems. However, the fine print is not all straight forward. There are not all scenarios which can be replicated into Central Finance. For eg, the transactional postings on Asset Sub ledger and WBS Elements through direct replication is not yet supported in central finance. There are quite a few challenges for customers, who already have SAP Source system which have parallel ledgers implemented. In such cases, the fiscal year differe nce in multiple ledgers presents its own issues. Some of the challenges assigned in Transactional data postings are:
◈ Asset Subledger postings are not supported in S/4HANA Central Finance. The posting on asset sub ledger in the source system have to be replicated on a normal GL Accounts in the target central finance system. We utilized the Key Mapping functionality in MDG Layer in Central Finance to ensure that the postings happened correctly
◈ The Transactional postings on WBS System in the source are not replicated into Central finance. This is mapped as a functionality, which will be addressed in the new releases of Central Finance. A custom enhancement was done in one of our projects to create the postings on other supported cost objects like internal order.
◈ Some of the legal entities had multiple ledgers in the source system with both ledgers having different fiscal year variants (one corresponding to 5-5-4 set up and other being April – March). The specification of the cutover month in source system for balance upload and document replication start due to different fiscal years in leading and non leading ledger meant duplicate data being posted in the non leading ledger, since the balance upload happens based on the fiscal year set up for leading ledger.
◈ A big challenge faced was the replication of the open items on the sub ledger and GL. The original document in source might be open at the time of initial load, but cleared in the period replication started. Such practical issues led to document failures in replication when subsequent actions on open items are not replicated immediately in central finance. These have been resolved through implementation of correction notes and custom code involvement
However, there are series of multiple challenges, which need to be considered in implementation of Central Finance. Some of them can dearly cost the S/4HANA Journey and cost thousands of dollars in terms of effort and missed objectives. Some of the business related challenges and technical product related challenges that I have encountered in my journey on Central Finance Project are below:
1. Organizational Structure: One of the biggest use cases for central finance is to look at harmonized reporting for multiple markets. A logical extension of central finance on S/4HANA is to use the same CFIN System as a future Business System with integrated Finance and logistics transaction system. Therefore, it makes the organizational structure design extremely critical. In one of my projects, the customer in the legacy ERP (Source SAP ERP Systems) was using Business Area, Segment, Profit center etc as key considerations for reporting. Additionally, the Logistics Org Structures like Sales Org were not having in synch in various Source ERP System, as well as non SAP Source system did not have the org object which were relevant from SAP standpoint. As an IT Strategy roadmap, the customer wanted all the markets, where it operated to be on S/4HANA Business Suite and CFIN was the starting point. Additionally, many of the org structures were used in Account Based COPA in CFIN. So the Organizational structure design is a very crucial factor for long term journey and it is critical that design of org structure is thought through in CFIN. This should take into consideration the future logistics org structure as well
2. New GL and Document Splitting in S/4HANA Central Finance: Document splitting and parallel ledgers functionality is one of the key asks from Finance Transformation for a large scale Enterprise level customer. Many of the customers might be using a source system without functionalities like new GL or Document splitting, but would want to use the S/4HANA CFIN with these functionalities. However a source system without Document splitting for eg and a target CFIN System with Document splitting is NOT a functionality which is supported out of box. It takes a real challenge to make sure that all the documents replicated from the source SAP ERP and non SAP Systems have the right level of details to support Document splitting. There are options available like BADI_FINS_CFIN_AC_INTERFACE, which can be used to enable the right rules for populating the account assignments for Document splitting. Some of the examples for Document splitting and parallel ledger usage:
◈ The account assignments for Document splitting can be populated only in some of the line items and let standard Splitting set up take care of offsetting line item (eg, Profit Center and segment update in line items and let vendor line item derive the same from offsetting line item in case of Vendor Invoice Posting).
◈ Some of the FI Document line items can derive account assignment objects for document splitting from areas like material master, cost center etc. The customer specific changes, should not be triggered in case, where standard derivation logic can work
◈ Secondary CO Postings from Source systems, where the profit center is not available in one of the line items, the customer specification needs to be updated
◈ Data from Non SAP systems needs to be enriched with account assignment details for postings in the target central finance system
◈ There are transfer postings between subledgers which fail in the target system if it has document splitting active.
3. Master Data Harmonization: Master data replication of objects like Cost Center, Profit center, GL Accounts, customers, Vendors etc is a challenge. Data harmonization is a key challenge in Enterprise customers with multiple SAP Systems. Some of the challenges in master data set up in Central Finance encountered in my experience are:
◈ Customer Vendor Integration - The central finance function was used in S/4HANA 1610 EM instance, where the customers and vendors are created as Business Partners and the number ranges were overlapping in the source system for Customer and vendor account groups. To tide over the issue, the number ranges for Vendors were changed in the target CFIN System
◈ GL Master Data Replication - The SAP ERP System were substantially old systems, where transactional data existed for more than 15 years. As part of CFIN replication, only few years of historical data was being replicated into the target CFIN System. So the GL Master replication was designed based on the no of years in past where transactional data existed for a GL, that only was replicated into the target system
◈ Profit Center and Segments – One of the outcome of org structure redesign in CFIN was the whole profit center and segment usage in Central finance. The profit center in target CFIN system was tagged to Brand for reporting, while a segment was concentrated around line of business. However, the brands in the source system were limited to profit center with Business area being used for line of business reporting. The usage of different objects for reporting in source and target system entailed usage of complex mapping framework for replication of master data
◈ Material master – The material master usage was also a challenge due to disparate systems. A governance structure was required to be put in place to synch up the master data in the source systems and than have the same replicated in the target system.
◈ Data Services or SLT for Master Data – Harmonization and Business Objectives for Master data usage greatly determined the usage of the technology layer for replication between Source SAP and non SAP Systems to S/4HANA Central Finance Environment. Based on specific requirements like Data Filters for GL Account, Numbering changes etc, it was decided to introduce Data Services as a technology layer between Source and Target system for master data replication in S/4HANA Master Data replication.
1. MDG Layer and Value / Key Mappings: Central Finance offers an integrated MDG layer which can be used to recreate the accounting document in the target system, based on the data replication from the source. Some of the key learnings from my association with the central finance project were:
◈ Mapping Action - The mapping action determines if a transformation is required for any data element. In one of my project, business area was very widely used for financial reporting in the source SAP system. However, the complete reimagining of financial reporting meant that business area was not a key reporting factor in Central Finance. Hence a mapping action was set to clear the business area information from the source data. Essentially, the Mapping action should be designed taking into consideration of what are the key financial reporting parameters and if those parameters will hold true for the business even in case of a completely integrated system of records with finance and logistics transactions happening in the same system some time into future.
◈ Key Mapping - Typically the identifiers for a business object can be different in source and target system, given that Central Finance has the ability to connect to a heterogeneous set of SAP and non SAP systems. Eg, a customer 2212 in a source system may be customer (BP) 500000 in CFIN to harmonize master data. In one of the projectw, the key ask was to manage millions of customer master, vendor, gl etc to name and arrive at a common structure. The current design of central finance does not support automatic mapping of the source and target object number, though there is a standard upload tool to do an excel upload using the transaction code FINS_CFIN_MAP_MANAGE. However, to manage the real time replication of master data in the mapping layer, a custom program was created for each of the object to ensure, that there are no failures in transactions
◈ Value Mapping Structure - The value mapping is used in Central Finance to ensure if any transaction specific value has to be transformed. In some of the projects, the source systems had custom values for objects like Document types, Tax Codes etc. The whole objective of the transformation program was to ensure a standardized approach to finance structure across multiple markets. Eg, the markets used Document type R1 and RX for billing in two different geographies, but the intention in the target central finance system was to ensure that all the geographies, where the business operated should have the same document type for billing transactions. Hence the value mapping functionality was used to ensure that the new system has a standardized approach
2. COPA Transformation from Costing based COPA to Account based COPA: Most of the customers in SAP World use Costing based COPA. However, the preferred approach for reporting in S/4HANA Is Account based COPA. The data replication from the Costing based COPA to Account based COPA is not a standard and out of box functionality in S/4HANA. Some of the challenges encountered have been:
◈ There are scenarios in CB COPA where COPA data and GL postings happen at different time, whereas the expectation on AB COPA is to have the data based in COPA and GL at the same time. This presented it’s own challenges since AB COPA was supposed to be used for all kind of profitability analysis. Some of the design considerations for this transformation included moving key data like Sales Area data, material product hierarchy etc from material master, customer sales area data into central finance. These attributes were used in the derivation rule to ensure that the right attributes are populated. In some of the scenario like post goods issue, the data which is relevant for COPA was pulled through custom enhancements into Central finance.
◈ There are condition types on the billing cycle, which post data into COPA but not into GL. This functionality is not yet supported in AB COPA in S/4HANA. This means that the business had to look at the way, in which some of the discounts and pricing could be extended to Billing cycle
3. Transactional Data Posting: Central finance is supposed to reflect all of transactional financial data into a single place from multiple systems. However, the fine print is not all straight forward. There are not all scenarios which can be replicated into Central Finance. For eg, the transactional postings on Asset Sub ledger and WBS Elements through direct replication is not yet supported in central finance. There are quite a few challenges for customers, who already have SAP Source system which have parallel ledgers implemented. In such cases, the fiscal year differe nce in multiple ledgers presents its own issues. Some of the challenges assigned in Transactional data postings are:
◈ Asset Subledger postings are not supported in S/4HANA Central Finance. The posting on asset sub ledger in the source system have to be replicated on a normal GL Accounts in the target central finance system. We utilized the Key Mapping functionality in MDG Layer in Central Finance to ensure that the postings happened correctly
◈ The Transactional postings on WBS System in the source are not replicated into Central finance. This is mapped as a functionality, which will be addressed in the new releases of Central Finance. A custom enhancement was done in one of our projects to create the postings on other supported cost objects like internal order.
◈ Some of the legal entities had multiple ledgers in the source system with both ledgers having different fiscal year variants (one corresponding to 5-5-4 set up and other being April – March). The specification of the cutover month in source system for balance upload and document replication start due to different fiscal years in leading and non leading ledger meant duplicate data being posted in the non leading ledger, since the balance upload happens based on the fiscal year set up for leading ledger.
◈ A big challenge faced was the replication of the open items on the sub ledger and GL. The original document in source might be open at the time of initial load, but cleared in the period replication started. Such practical issues led to document failures in replication when subsequent actions on open items are not replicated immediately in central finance. These have been resolved through implementation of correction notes and custom code involvement