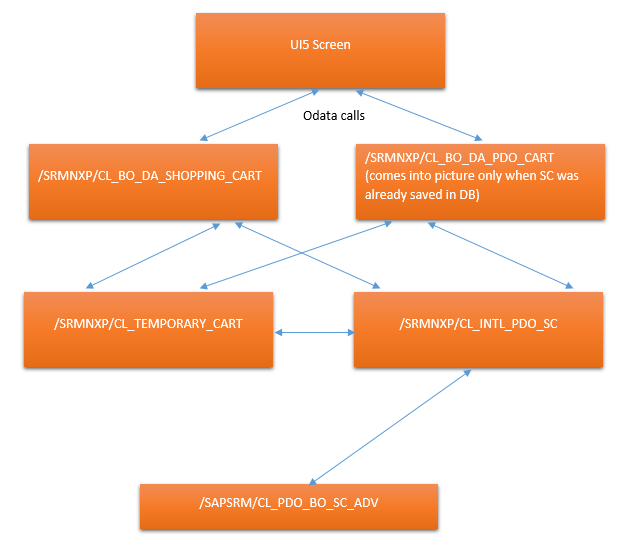
I am going to share some helpful information for SRM UI5 Add-on developers ( with ABAP knowledge ) about important classes that you need to remember while debugging any issues related to SC creation and also how these classes communicate with each other and their purpose in overcall SC creation.
There are five important class involved.
/SRMNXP/CL_BO_DA_SHOPPING_CART: this class is runtime class for SRMSHOPPING_CART OData service (responsible for entity types ShoppingcartItemCollection and ShoppingcarCollection) that is responsible for SC creation. So everything starts and end in this class. Data entered on the UI5 screen is passed to this class and also data that is to be displayed finally in the screen is passed back to this class. Inside most of the methods of the class the actual work is delegated to /SRMNXP/CL_TEMPORARY_CART and /SRMNXP/CL_INTL_PDO_SC.
/SRMNXP/CL_BO_DA_PDO_CART: This class has same purpose as above class but is responsible for entity types SRMShoppingcartItemCollection and SRMShoppingcarCollection. This class comes into picture, if you are adding item to a SC which was already saved in database or when you click on item details or any other tab in the item details.
/SRMNXP/CL_TEMPORARY_CART: This class manages the temporary cart until it is completely ordered or SAVE&CLOSE button is clicked or entire minicart is deleted. This class communicates with class /SRMNXP/CL_BO_DA_SHOPPING_CART and /SRMNXP/CL_INTL_PDO_SC.
/SRMNXP/CL_INTL_PDO_SC: This class acts as an intermediate layer (I assume that is the reason for INTL in its name) between /SRMNXP/CL_TEMPORARY_CART and /SAPSRM/CL_PDO_BO_SC_ADV.
/SAPSRM/CL_PDO_BO_SC_ADV: This is our old PDO friend that is responsible for creation of SC in SRM (this class existed since golden era of webdynpro in SRM 7.0).
/SRMNXP/CL_BO_DA_SHOPPING_CART: this class is runtime class for SRMSHOPPING_CART OData service (responsible for entity types ShoppingcartItemCollection and ShoppingcarCollection) that is responsible for SC creation. So everything starts and end in this class. Data entered on the UI5 screen is passed to this class and also data that is to be displayed finally in the screen is passed back to this class. Inside most of the methods of the class the actual work is delegated to /SRMNXP/CL_TEMPORARY_CART and /SRMNXP/CL_INTL_PDO_SC.
/SRMNXP/CL_BO_DA_PDO_CART: This class has same purpose as above class but is responsible for entity types SRMShoppingcartItemCollection and SRMShoppingcarCollection. This class comes into picture, if you are adding item to a SC which was already saved in database or when you click on item details or any other tab in the item details.
/SRMNXP/CL_TEMPORARY_CART: This class manages the temporary cart until it is completely ordered or SAVE&CLOSE button is clicked or entire minicart is deleted. This class communicates with class /SRMNXP/CL_BO_DA_SHOPPING_CART and /SRMNXP/CL_INTL_PDO_SC.
/SRMNXP/CL_INTL_PDO_SC: This class acts as an intermediate layer (I assume that is the reason for INTL in its name) between /SRMNXP/CL_TEMPORARY_CART and /SAPSRM/CL_PDO_BO_SC_ADV.
/SAPSRM/CL_PDO_BO_SC_ADV: This is our old PDO friend that is responsible for creation of SC in SRM (this class existed since golden era of webdynpro in SRM 7.0).